CAR
Via A1/E45, exit Battipaglia. Follow SS 18 Tirrena Inferiore, SS18var and SP66 towards SP164 in Camerota
Via Lentiscella, 3, 84059 Marina di Camerota SA

Via A1/E45, exit Battipaglia. Follow SS 18 Tirrena Inferiore, SS18var and SP66 towards SP164 in Camerota
Take the train in the direction of Sapri. Proceed by bus to Camerota (San Vito)
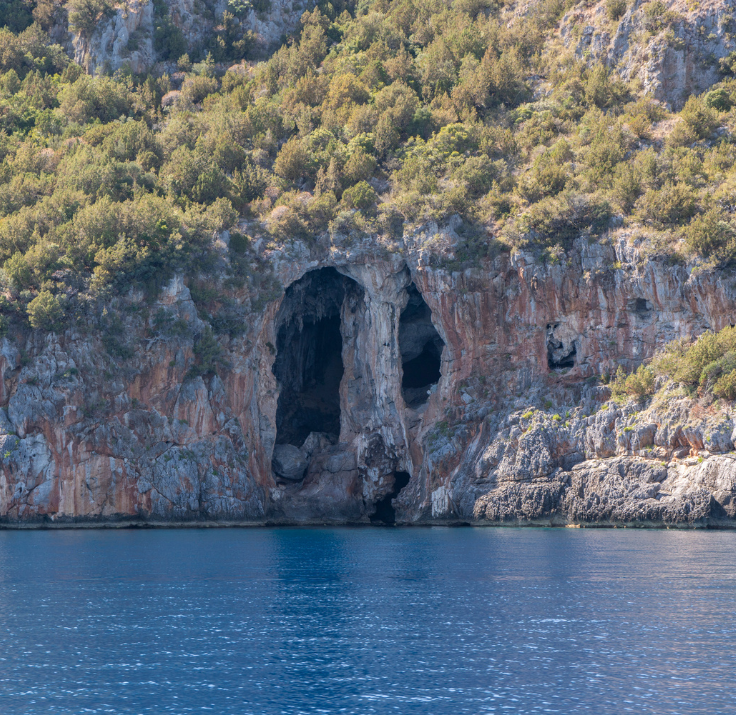
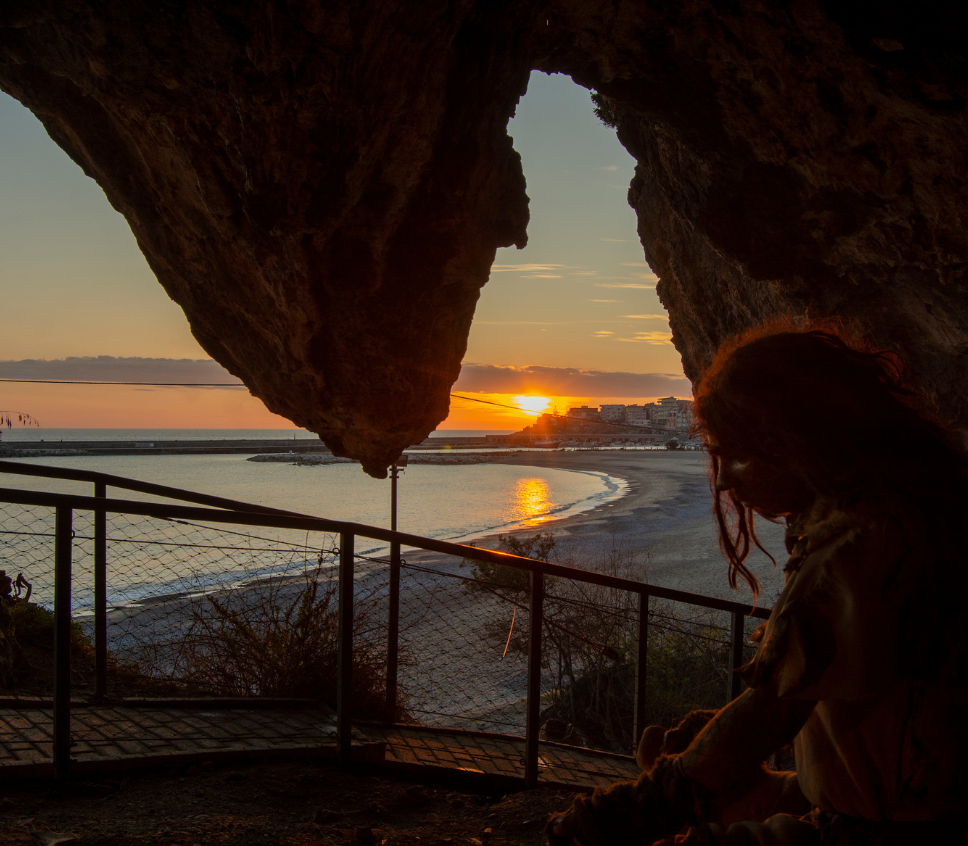
The first excavations of the Cove Cave were carried out by A. Palma of Cesnola in 1966-1969. Since then, the researches continued. Cove Cave is a few meters away from the sea. The map of the cavern has an hourglass shape and is made up of an ante-cavern and a retro- cavern, connected by a narrowing. The archeological evidences indicate an initial frequentation by Neanderthal groups in the Middle Palaeolithic and more systematic use of the cave by the first Homo Sapiens (around 30,000 to 10,000 years ago).
The most significant layers are those of a particular Upper Paleolithic cultural period, called Gravettian, between 27.000 and 24.000 years ago. These leyers are characterized by a wide variety of stone tools, such as scrapers and back spikes, abundant faunal remains, sea shells used as decorations, bone artifacts and fireplaces. The hounting economy was mainly based on the exploitation of deer. Intresting finds came from the most recent layers: a painted pebble from the Mesolithic, a child burial from the Neolithic and from the following Copper Age some ceramic containers and some bone weapons, refined by the fish-like shape of the attachment to which the fishing line is attached.
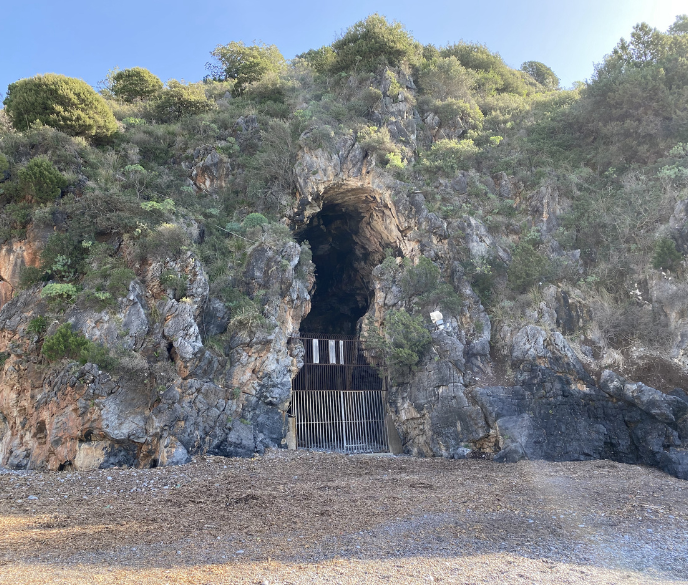
By crossing a wooden boardwalk it is possible to walk along a path inside the cavern among excavation still in progress, tools and reproductions of primitive hominids. The exhibition, with mannequins with clothes and features of cavemen, was curated two years ago by experts from the University of Siena, in sinergy with the Superintendence and the direction of the Virtual Palaeolithic Museum of of Camerota.
The area near the Cove Cave is occupied by a deciduous forest (Quercus). Whereas the innermost mountain slopes host a coniferous forest (Pinussylvestris). Insectivores (Glis) are particularly common. The fishing industry includes points and scrapers, mostly of levallois tecnique. It is most probably a typical Mousterian.